Your Thin film interference equation images are available. Thin film interference equation are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Find and Download the Thin film interference equation files here. Find and Download all royalty-free photos.
If you’re searching for thin film interference equation pictures information related to the thin film interference equation keyword, you have come to the ideal blog. Our site always provides you with suggestions for seeing the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly hunt and locate more informative video content and graphics that match your interests.
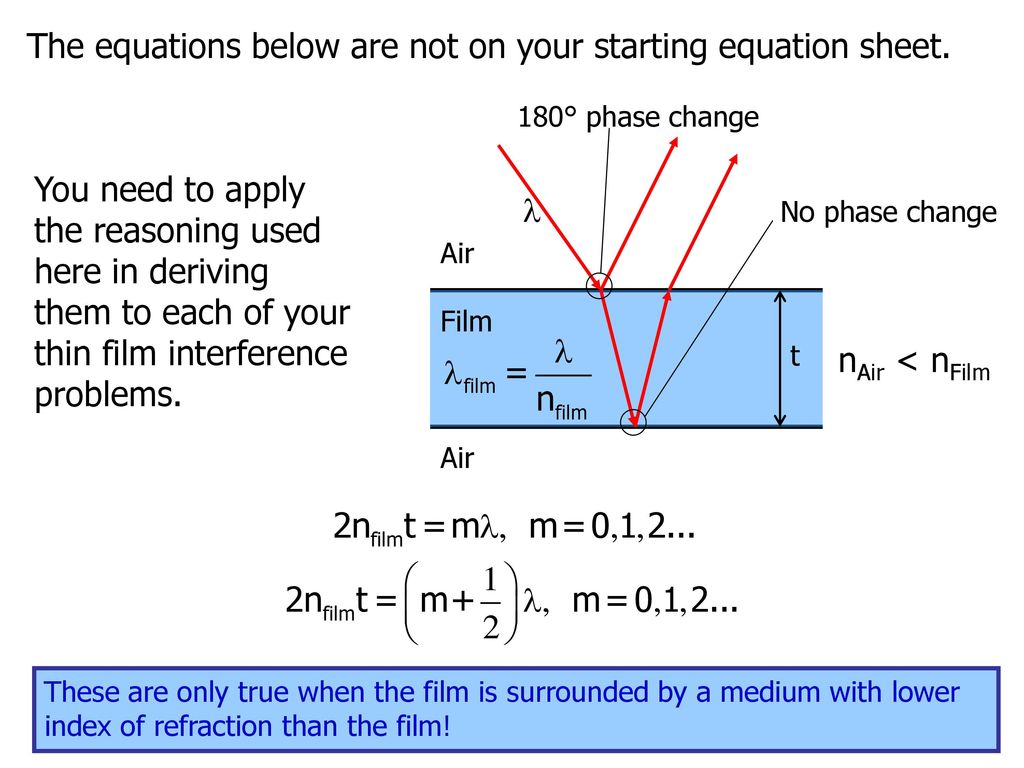
Thin Film Interference Equation. Thin Film Interference 12 n1 n2 n3 n1. If the path difference is 12 wavelength then that adds a 180 degree phase shift which added to the original 180 degree phase difference puts them in phase. Phase shift of the two reflected waves is 180oã for such a glass coating with normal incidence we must for constructive interference 2 NCOAT T MI  m 012 and by destructive interference we need 2 ncaat t m ½ i  m 12. Note below that the reflection when traveling from air at n1 to oil at n 14 experiences the phase change but from oil to water at n 133 there is no phase change.
 Today S Agenda Thin Film Interference Ppt Download From slideplayer.com
Today S Agenda Thin Film Interference Ppt Download From slideplayer.com
Minima 2 2t m 1 n air. And thats the key to thin films. The equation can now be solved. If the angle of incidence on the film is α the index of refraction of the film is n the thickness of the film is d micrometers and the order of wavelengths m then the angle in the film is β from Snells law The wavelength for maximum reflection is λr nm. Constructive interference formula thin film Destructive interference formula thin film When the OPD or optical path difference between the two waves is equal to an integral multiple of the given wavelength of light ie. V cn where v is the speed of light in the medium c is the speed of light in a vacuum 3x108 ms and n is the index of refraction.
Phase shift of the two reflected waves is 180oã for such a glass coating with normal incidence we must for constructive interference 2 NCOAT T MI  m 012 and by destructive interference we need 2 ncaat t m ½ i  m 12.
The equation can now be solved. Interference maxima and minima. Phase shift of the two reflected waves is 180oã for such a glass coating with normal incidence we must for constructive interference 2 NCOAT T MI  m 012 and by destructive interference we need 2 ncaat t m ½ i  m 12. This is not the only thickness that gives completely constructive interference for this wavelength. Light on thin films. Thin Film Interference 12 n1 n2 n3 n1.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Light on thin films. Light on thin films. Constructive interference if phase change. Minima 2 2t m 1 n air. So where do I have constructive interference.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
The light reflected from any one. Constructive interference formula thin film Destructive interference formula thin film When the OPD or optical path difference between the two waves is equal to an integral multiple of the given wavelength of light ie. Air soap air bright fringes 2t m Maxima. Using their derivation of the Fresnel and interference equations for that specific situation as a guide for my purposes the following was found. So where do I have constructive interference.
 Source: labman.phys.utk.edu
Source: labman.phys.utk.edu
Minima 2 2t m 1 n air. The optical properties of thin films arise from interferenceand reflection. When the film is excessively thin such that its thickness t. If the path difference is 12 wavelength then that adds a 180 degree phase shift which added to the original 180 degree phase difference puts them in phase. So where do I have constructive interference.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
A couple of wavelengths of light Condition for maximum bright fringe. Note below that the reflection when traveling from air at n1 to oil at n 14 experiences the phase change but from oil to water at n 133 there is no phase change. If the path difference is 12 wavelength then that adds a 180 degree phase shift which added to the original 180 degree phase difference puts them in phase. If the angle of incidence on the film is α the index of refraction of the film is n the thickness of the film is d micrometers and the order of wavelengths m then the angle in the film is β from Snells law The wavelength for maximum reflection is λr nm. Hat n_x costheta_x u_x iv_x where beginalign 2u_x2 a_x sqrt a_x2 4 b_x2 2v_x2 -a_x sqrt a_x2 4 b_x2 endalign and beginalign.
 Source: physics.stackexchange.com
Source: physics.stackexchange.com
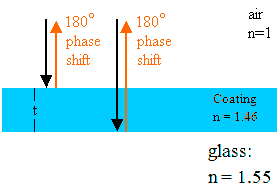
When the path difference is an integer 12 number of wavelengths. Air soap air bright fringes 2t m Maxima. The basic conditions for interferencedepend upon whether the reflections involve 180 degree phase changes. In this situation we are asked to find the minimum thickness of the film. λ n.

The two reflected waves interfere constructively Minimum. Minima 2 2t m 1 n air. If the angle of incidence on the film is α the index of refraction of the film is n the thickness of the film is d micrometers and the order of wavelengths m then the angle in the film is β from Snells law The wavelength for maximum reflection is λr nm. When the film is excessively thin such that its thickness t. Using their derivation of the Fresnel and interference equations for that specific situation as a guide for my purposes the following was found.

And thats the key to thin films. The two reflected waves interfere constructively Minimum. Thin Film Interference 12 n1 n2 n3 n1. When light hits a material that has multiple layers each layer can reflect light. And thats the key to thin films.

Hat n_x costheta_x u_x iv_x where beginalign 2u_x2 a_x sqrt a_x2 4 b_x2 2v_x2 -a_x sqrt a_x2 4 b_x2 endalign and beginalign. In this situation we are asked to find the minimum thickness of the film. This is not the only thickness that gives completely constructive interference for this wavelength. Thin Film Interference 12 n1 n2 n3 n1. For a thick film thickness a t 14 Þ  ncoat we obtain a net change of ½ wavelength.
 Source: sciencecalculators.org
Source: sciencecalculators.org
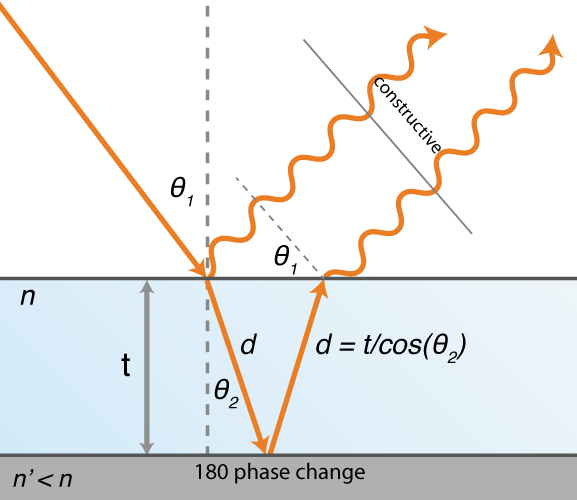
Standard analysis of Thin Film Interference 1 1 1 2 2 Max constructive 2 Min destructive n n dm dm λ λ d n 1 n 2 Angle shown but actually n normally incident 0 1 1 1 n n λ λ Wavelength inside film. Standard analysis of Thin Film Interference 1 1 1 2 2 Max constructive 2 Min destructive n n dm dm λ λ d n 1 n 2 Angle shown but actually n normally incident 0 1 1 1 n n λ λ Wavelength inside film. Interference maxima and minima. The light reflected from any one. Thicknesses on the order of 01 μm10 μm ¼λ10λ of visible light within the film are considered thin.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
Constructive interference formula thin film Destructive interference formula thin film When the OPD or optical path difference between the two waves is equal to an integral multiple of the given wavelength of light ie. Using their derivation of the Fresnel and interference equations for that specific situation as a guide for my purposes the following was found. Thin film interference occurs when light reflects multiple times off the two sides of a thin transparent material. Thin film interference can be both constructive and destructive. This is not the only thickness that gives completely constructive interference for this wavelength.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
The equation can now be solved. Thicknesses on the order of 01 μm10 μm ¼λ10λ of visible light within the film are considered thin. This phase change is important in the interferencewhich occurs in thin films the design of anti-reflection coatings interference filters and thin film mirrors. Interference maxima and minima. The equation can now be solved.

So where do I have constructive interference. Thicknesses on the order of 01 μm10 μm ¼λ10λ of visible light within the film are considered thin. Constructive interference if phase change. Phase shift of the two reflected waves is 180oã for such a glass coating with normal incidence we must for constructive interference 2 NCOAT T MI  m 012 and by destructive interference we need 2 ncaat t m ½ i  m 12. So where do I have constructive interference.

The optical properties of thin films arise from interferenceand reflection. This phase change is important in the interferencewhich occurs in thin films the design of anti-reflection coatings interference filters and thin film mirrors. Minima 2 2t m 1 n air. For a thick film thickness a t 14 Þ  ncoat we obtain a net change of ½ wavelength. When light hits a material that has multiple layers each layer can reflect light.

Thin film interference Thin. This means choosing the minimum value of m which in this case is m 0. Light on thin films. The basic conditions for interferencedepend upon whether the reflections involve 180 degree phase changes. So where do I have constructive interference.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
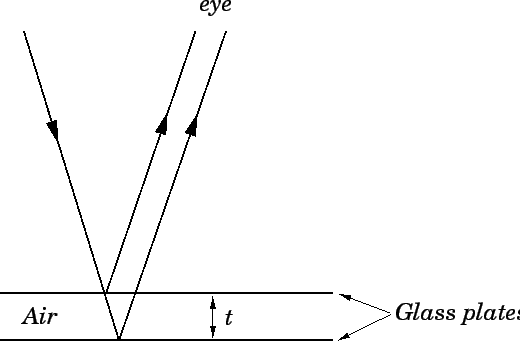
The equation can now be solved. D Interference due to an infinitely thin film When the thin of the film is small compared to the wave length of light t. The light reflected from any one. Standard analysis of Thin Film Interference 1 1 1 2 2 Max constructive 2 Min destructive n n dm dm λ λ d n 1 n 2 Angle shown but actually n normally incident 0 1 1 1 n n λ λ Wavelength inside film. Phase shift of the two reflected waves is 180oã for such a glass coating with normal incidence we must for constructive interference 2 NCOAT T MI  m 012 and by destructive interference we need 2 ncaat t m ½ i  m 12.
 Source: farside.ph.utexas.edu
Source: farside.ph.utexas.edu
Thin film interference can be both constructive and destructive. Note below that the reflection when traveling from air at n1 to oil at n 14 experiences the phase change but from oil to water at n 133 there is no phase change. Phase shift of the two reflected waves is 180oã for such a glass coating with normal incidence we must for constructive interference 2 NCOAT T MI  m 012 and by destructive interference we need 2 ncaat t m ½ i  m 12. Thicknesses on the order of 01 μm10 μm ¼λ10λ of visible light within the film are considered thin. Interference maxima and minima.

Constructive interference if phase change. So where do I have constructive interference. The basic conditions for interferencedepend upon whether the reflections involve 180 degree phase changes. Thicknesses on the order of 01 μm10 μm ¼λ10λ of visible light within the film are considered thin. Equations to relate the thickness of the film angle of refraction and wavelength of light that experiences either constructive or destructive interference.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Air soap air bright fringes 2t m Maxima. Thicknesses on the order of 01 μm10 μm ¼λ10λ of visible light within the film are considered thin. Thin film interference can be both constructive and destructive. Minima 2 2t m 1 n air. In this situation we are asked to find the minimum thickness of the film.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site good, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title thin film interference equation by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






